Calling scripts lets you share common actions between scripts and eliminate the need to re-create tests when an application changes. As a best practice, try to create simple, modular scripts that focus on performing a specific task. After you create scripts to perform different tasks, you can use the Script.CallScript statement to combine them and create more complex scripts that perform multiple tasks at the same time.
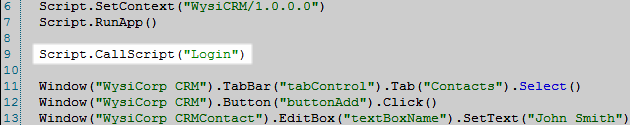
For example, if you are testing a web application that requires logging in, you can create a login script that can be called from other scripts in the workspace. When the login script is called, QA Wizard Pro runs it to completion and then returns to the script that called it to continue playback. If errors occur during login or the login process changes in the application, you only have to update the login script instead of all scripts that use the same steps. The following example shows a script with the Script.CallScript statement that calls another script named Login.

Note: You can call standard QA Wizard Pro scripts from load test scripts and vice versa. If a load test script is called from a standard script, the load test script runs normally but with only one user.
1. Select the script line above where to add the statement.
2. Choose Script > Add Statement.
The Add Statement dialog box opens.
3. Select the Script Call Script statement from the Script Control category.
4. The Application/version field is automatically set with the context. This information is used to populate the Window and Control fields on the Add Statement dialog box with values from the application repository.
If QA Wizard Pro cannot identify the context, None is selected. This usually occurs when you add statements to a utility script that is only called by other scripts because the context is set in the script that calls it. If an application/version is required, select it from the list.
5. Select the Script name to call.
6. If the script uses an associated datasheet to perform data-driven actions, select Constant from the value list in the Optional datasheet name field and select the datasheet.
Data sources associated with called scripts are ignored unless you specify a datasheet for them in the Script.CallScript statement. If a datasheet is specified, the called script runs once for each row in it. If a datasheet is not specified, the called script only runs once, but has access to the variables and data source associated with the calling script and any statements declared before the Script.CallScript statement.
7. Click OK to add the statement to the script.
Tip: You can also drag a script from the Workspace pane to the open script to automatically add a Script.CallScript statement.